MATLAB Code
% The code is written by SalimWireless.Com
% Clear previous data and plots
clc; % Clear the command window
clear all; % Remove all variables from the workspace
close all; % Close all figure windows
% Parameters
Tb = 1; % Bit duration in seconds
fc = 10; % Carrier frequency in Hz
N = 10; % Number of bits to transmit
% Generate carrier signal
t = 0:Tb/100:1; % Time vector for one bit duration with 100 samples
carrier_signal = sqrt(2/Tb) * sin(2*pi*fc*t); % Normalized carrier signal
% Generate message signal
rng(10); % Set random seed for reproducibility
binary_data = rand(1, N); % Generate random binary data between 0 and 1
% Initialize time intervals for message bits
t_start = 0;
t_end = Tb;
% Loop to generate and modulate each bit
for i = 1:N
t = t_start:0.01:t_end; % Time vector for current bit duration
% Generate binary message signal (1 or 0)
if binary_data(i) > 0.5
binary_data(i) = 1;
message_signal = ones(1, length(t)); % Bit value 1
else
binary_data(i) = 0;
message_signal = zeros(1, length(t)); % Bit value 0
end
% Store message signal
message(i,:) = message_signal;
% Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) modulation
ask_signal(i,:) = carrier_signal .* message_signal;
% Update time intervals for next bit
t_start = t_start + (Tb + 0.01);
t_end = t_end + (Tb + 0.01);
end
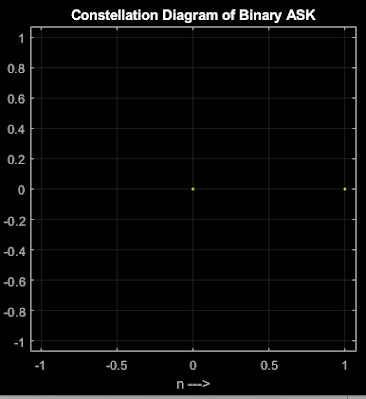
% Constellation Diagram
figure(1);
scatterplot(binary_data); % Scatter plot of transmitted binary data
title('Constellation Diagram of Binary ASK');
xlabel('n --->'); % X-axis label
ylabel('b(n)'); % Y-axis label
grid on; % Enable grid
% Effect of noise on ASK constellation diagram
channelAWGN = 15; % SNR value for AWGN channel
rxData2 = awgn(binary_data, channelAWGN); % Add AWGN to binary data
figure(2);
scatterplot(rxData2); % Scatter plot of noisy received data
title('Effect of noise on ASK constellation diagram');
xlabel('n --->'); % X-axis label
ylabel('b(n)'); % Y-axis label
grid on; % Enable grid
Output
Copy the MATLAB Code from here
Also read about
[1] Constellation Diagram of ASK