Overview
Sky Wave, Microwave Link Communication, and Satellite Communication (SATCOM) are the focus of this article. Sky Waves are essentially AM waves that the ionosphere reflects. For long-distance communication on Earth, we employ standard microwave link transmission. However, we all know that the earth is not flat, but rather oval in shape. As a result, the signal can only reach a few kilometers on a straight line of sight path (LOS). The signal is then reflected by the earth's surface. But we know that with that microwave link, we can communicate hundreds of kilometers distance. We'll look at how this happens in this article. Terrestrial satellite communication has now replaced microwave relay link communication.
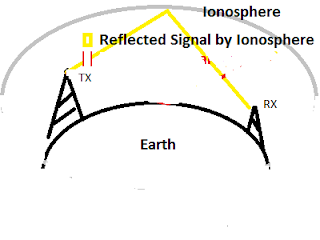
Figure: Ionosphere Reflection - suitable for AM band (Sky Wave)
1. Sky Wave
You can see how the ionosphere bounces the radio signal and enables the ground station to communicate with the transmitter hundreds of kilometers away. This method is ideal for communication at low or medium frequencies. Ionosphere reflects low (AM band) or medium (<30 MHz) range frequency.
Due to its high frequency, the microwave band cuts through the ionosphere, making it ideal for communicating with satellites. However, with the help of the ionosphere, we can efficiently receive a signal at a distance of roughly 650 kilometers from the transmitter.
1.1. Role of Ionosphere for Sky Wave
The ionosphere is one of the top levels of the earth's atmosphere, as we all know. Its altitude ranges from 30 to 600 miles above the earth's surface. We, as humans, reside in the troposphere. Atoms and molecules in the ionosphere are electrically charged. The ionosphere has the unique property of reflecting radio signals below 30 MHz. Signals with operating frequencies greater than 30 MHz penetrate the ionosphere layer. Also, do not return to Earth. In this situation, we always keep the frequency below 30 MHz. When we send a signal via a microwave link, the earth's ionosphere reflects it. In the diagram above, the transmitter emits a signal, which is then reflected by the ground and, in a similar way, by the ionosphere. According to our knowledge, a received signal reflected by the ionosphere is easier to receive by a receiver than a reflected signal by the ground.
.png)
.png)
