1. Analog Beamforming:
Beamforming is a method of focusing a signal in a certain direction to provide sufficient signal strength at the receiver end of the communication process. We normally require more than one closely located antenna to form a beam in a specific direction and focus the resultant signal from antennas to use beam forming. We can also use a phase shifter or PSs to control the phases of a signal. We employ MIMO (multiple input multiple output antenna) [↗] to provide beam forming. In a MIMO system, antennas are normally positioned in a half-wavelength interval of the operating frequency.
We commonly employ beam forming when we need to send a signal over a great distance (e.g., for radar communication) and omnidirectional transmission isn't feasible. On the other hand, we can use beam forming to extend the range of our signal without boosting TX power.
Similarly, 5G communication [Read More] makes advantage of an incredibly high frequency [↗]. As a result, it suffers from severe path loss [↗], and its short wavelength is easily absorbed by air gases, vapor, and other particles. With sufficient power, such an extremely high-frequency band can only go a short distance. As a result, we use beam forming to cover greater distances. We get a stronger and narrower beam by increasing the number of antennas without raising the TX power. It is an important advantage of beamforming.
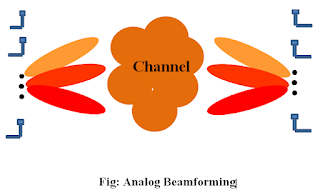
There are several methods of beam formation, but they are usually divided into three categories: 1. Analog beam forming 2. Digital Beamforming 3. Hybrid Beamforming. In analog beam formation, the beam is steered at both the transmitter and receiver end, and the best beam pairs are selected for communication. More simply, we aim to send signals at varying angles of arrival range, or AOA, from the transmitter side. We do the same thing on the receiver side, then only connect the best beams from both the transmitter and receiver sides. We can only change the phases (or, to put it another way, the direction of signal transmission) of a signal in analog beam forming, and there is only one data stream between the transmitter and receiver.
Get MATLAB Code for Analog and Digital Beamforming
The number of antennas on both the transmitter and receiving sides may be seen in the diagram above. To form a beam, more than one neighboring antenna is required, as previously stated. The fact that there is just one RF Chain on both the transmitter and receiver sides is a crucial aspect of analog beam formation. The number of RF chains equals the number of simultaneous data streams accessible between the transmitter and receiver. In the diagram above, we steer the beam at the transmitter to find the optimal beam between the transmitter and the receiver, while the receiver transmits in an omnidirectional manner. The same thing happens at the receiver's end, or the receiver tries directional beams while the transmitter radiates in an omnidirectional manner. Then, using adequate feedback, the best beam pairs from both sides are connected. RF chains contain mixers, power amplifiers, etc.
In the following chapters, we'll look into digital beam forming, which allows multiple data streams to be sent and received simultaneously. We'll also talk about canceling interference between many devices and canceling interference between simultaneous data streams.
2. Digital Beamforming:
Unlike analog pre-coding, we can send signals with a variety of phases and amplitudes. Different phases signify different things, such as the ability to steer the beam in different directions, which is also accessible for analog beam formation. On the other side, we can also regulate the transmitted signal's amplitude. If we need to reduce the signal's amplitude in a specific antenna element, we can easily do it.
The signal that was received is denoted by
y=√pHDs + n
where, p=average received power
H=channel matrix
D= digital or baseband pre-coder
s= symbol vector
n = additive white Gaussian noise
Each antenna is connected to a distinct transmit and receive (TR) module or RF chain in the system diagram below.
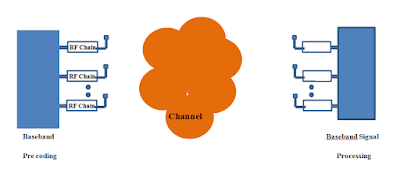
Fig: Digital Beamforming
We know that point-to-point communication between MIMO is conceivable, such as h11, h12, h22, and so on. For example, 'h22' denotes channel gain or the link between the second antenna on the transmitter and the second antenna on the receiver.
Also Read about
[1] What is the process of beamforming in MIMO or massive MIMO systems?
[3] Mathematical aspects of beamforming in MIMO
[4] Equations related to spectral efficiency in digital beamforming
[5] Equations related to spectral efficiency in hybrid beamforming
[6] MATLAB Codes for various types of beamforming
[7] Spatially Sparse Hybrid Precoding / beamforming
[8] What are the Precoding and Combining Weights / Matrices in a MIMO Beamforming System
[10] Beamforming in Audio Signal Processing
[11] MIMO, massive MIMO, and Beamforming
more ...
# analog beamforming